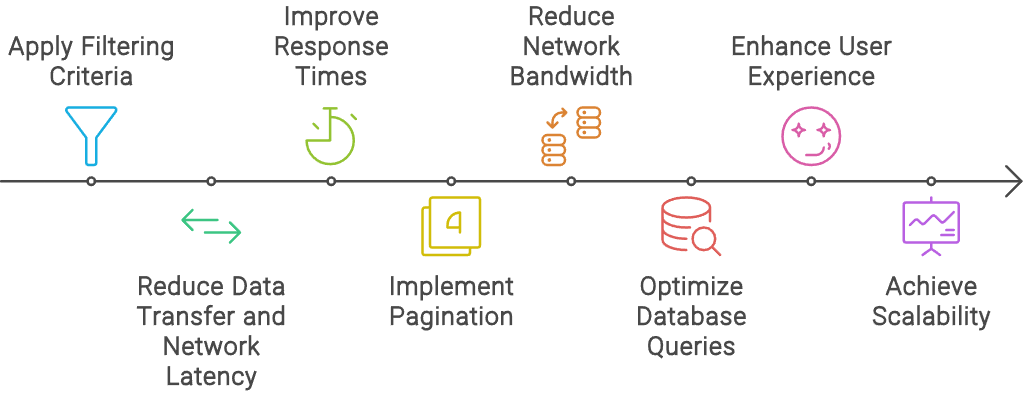
While client-side pagination may work for certain use cases, especially for smaller datasets, one must depend on server-side pagination for better performance, scalability, and security, especially when dealing with larger or sensitive datasets.
So, when exactly to use server-side pagination? Here are some situations:
Large Datasets
Server-side pagination is the key when dealing with large datasets. Using it will help you avoid loading the entire dataset into memory and transferring it to the client side. It helps you fetch only the necessary subset of data from the server, thus improving performance and reducing bandwidth consumption.
Another benefit of using server-side pagination is that it ensures that only a manageable chunk of data is processed and transferred over the network, thus improving the loading speed and offering a better user experience.
Scalability
Server-side pagination scales efficiently and are suitable for applications with a growing user base. By distributing the processing load on the server and churning out data in smaller chunks, it effectively handles high volume of website traffic and increasing data volume, without compromising performance.
The server can thus optimize database queries, apply caching mechanisms, and leverage indexing to efficiently retrieve and deliver paginated data to clients.
Security
Server-side pagination maintains data security by limiting access to sensitive information. The client only gets access for the requested page of data, thus restricting exposure to unauthorized users.
Server-side paging keeps your secret information safe on the server, not downloaded to everyone's devices. This prevents unauthorized access and makes it harder for hackers to steal confidential information.
Consistency
Server-side pagination keeps consistency when it comes to data presentation. This ensures that everyone sees the same data on each page, no matter what device they're using, their device capabilities or configurations.
This consistency enhances user experience and facilitates seamless navigation through paginated data.
Optimization
Server-side pagination enables optimization of database queries, reducing the overhead of retrieving and processing large datasets. Server-side paging helps the server work smarter, not harder. It uses indexing, filtering, and sorting to minimize database load and improve query performance.
Additionally, it allows implementation of caching mechanisms to optimize data retrieval and improve application performance.
Server-side pagination can be a safe bet when using applications with large datasets, requiring scalability, ensuring data security, maintaining consistency, and optimizing data retrieval and performance. It offers better control over data processing, thus improving its application scalability, and overall user experience.
However, different situations call for diverse techniques:
One can use different techniques and strategies, depending on the requirements and constraints of the app. This can offer better performance, scalability, and an ideal user experience. Here are some additional techniques:
Data Caching
Use caching mechanisms to store the data that you access frequently, store such data in memory or a distributed cache (e.g., Redis). This will reduce the need to fetch data repeatedly from the database, thus substantially improving the response times and reducing database load.
Here are some caching strategies one can use: in-memory caching, output caching, and query caching to level up their performance for different datasets and operations.
Data Denormalization
Denormalize database tables by storing redundant or precomputed data to optimize read performance. Denormalization reduces the need for complex joins and calculations at runtime, improving query performance and response times.
Analyze query patterns to identify any opportunities for denormalization and optimize data schema accordingly.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A CDN is like having smaller warehouses closer to different user bases instead of one giant warehouse. Use CDNs to cache and deliver static assets (e.g., images, CSS files, JavaScript files) closer to users, thus bringing down latency and improving load times. CDNs are distributed across a network of edge servers, ensuring speedy delivery to users irrespective of where they are located.
Integrate CDN support into the application architecture to provide static content efficiently and enhance the overall performance.
Asynchronous Processing
Asynchronous processing is like having some extra help in a busy restaurant with a single waiter. It offloads long-running or resource-intensive tasks in the background and frees up server resources, thus allowing the application to handle continuous requests more efficiently.
Implement asynchronous patterns such as message queues, background jobs, and event-driven architectures to decouple big components and improve the scalability of your application.
Load Balancing and Horizontal Scaling
Load balancing is like having a bunch of computers working together. Deploy load balancers and distribute the incoming traffic across multiple servers or nodes, ensuring optimal utilization and high availability of resources. This can significantly improve fault tolerance and scalability by evenly distributing requests among the available backend servers.
Implement horizontal scaling and add more server instances or nodes to your application infrastructure as its demand grows. This can help increase the application capacity and enable it to handle a high volume of concurrent user requests.
Query Optimization and Indexing
In this, websites ask questions to a big data room (database) to find what they need. It is important to optimize database queries by analyzing query execution plans, identifying performance bottlenecks, and optimizing SQL queries, joins, and indexes. Use database management tools to monitor and analyze the performance metrics of queries and identify optimization opportunities.
Create indexes on frequently queried columns to improve query performance and reduce the time required to fetch data from the database. Regularly review and update indexes based on usage patterns and query performance metrics.
Content Compression and Minification
Compress static assets like HTML, CSS, JavaScript) to reduce their file sizes and reduce network latency. Content compression techniques such as GZIP compression and Brotli compression can bring down the amount of data transferred over the network. This can significantly improve page load times and user experience.
Use server-side and client-side tools to automate content compression and compressing processes, thus ensuring optimal performance for web applications.
Progressive Rendering and Lazy Loading
Imagine a website loading piece by piece, like a picture slowly showing up. This lets you start using the website even before everything is finished downloading, making it feel faster. Implement progressive rendering techniques to prioritize loading and rendering critical content first to improve user engagement and perceived performance. It enables users to interact with the application while the additional content is being loaded.
Use lazy loading for non-essential or below-the-fold content to defer loading until it's needed, reducing initial page load times and conserving bandwidth. Lazy loading optimizes resource usage and improves overall performance for content-heavy pages.
Use these methodologies and strategies as per your specific requirements and application challenges. These techniques help developers optimize app performance, scalability, and user experience in general.
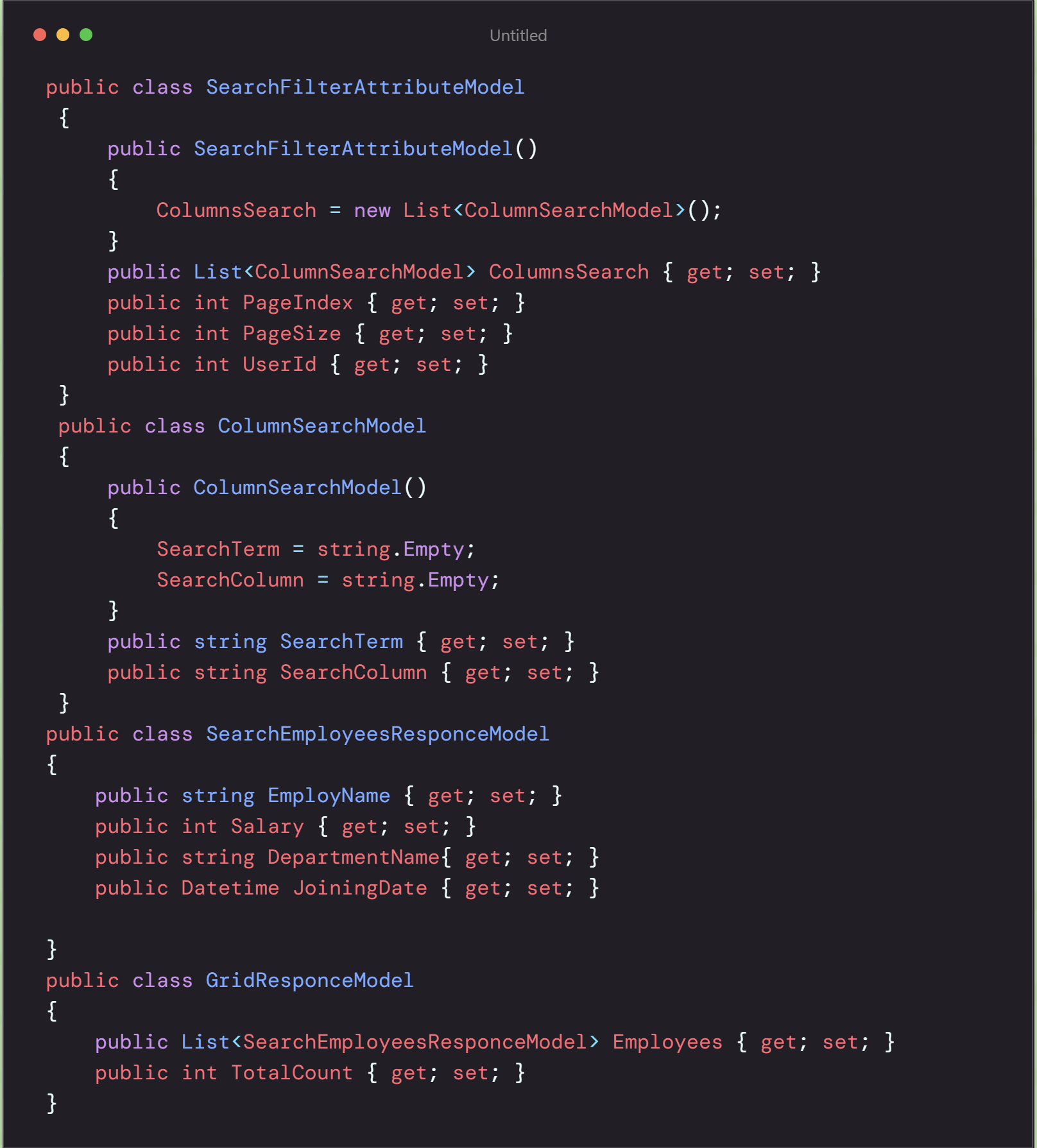
In this code,we have created ColumnSearchModel to filter multiple columns in which SearchTerm contains value and SearchColumn contains column name on which filter value apply.
SearchFilterAttributeModel is passing in API which contains List of ColumnSearchModel to filter multiple columns at a time, PageIndex is Page No. you want to show and PageSize is No. of records you want to show in a page and UserId is curruntly login user id.
SearchProfileResponceModel is user model that has columns you want to display in grid.
GridResponceModel is responce of API, which contains List of SearchProfileResponceModel and TotalCount. TotalCount is total records qualify when filters apply. after that paging will apply and returns user profiles.
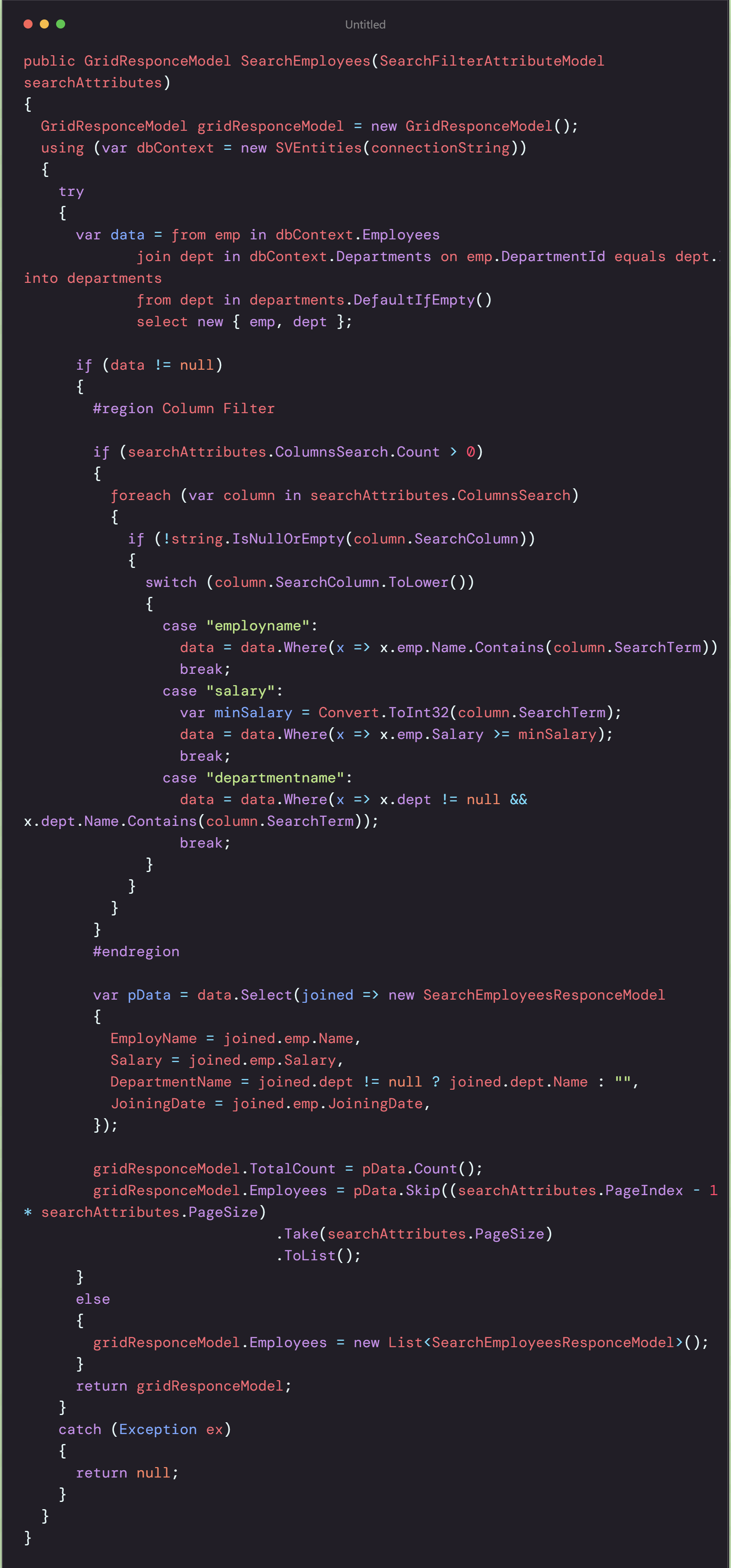
SearchProfile called with searchAttributes and returns gridResponceModel.
We will store linq query in data of joining multiple table.
it Joins two tables Employees and Departments as emp and dept.
we will only apply filter, if any ColumnSearchModel available.
For each column filter will apply by checking column name in Switch statement.
Filtering condtion apply on data query depending on column name.
Total count of calculated data passing in gridResponceModel.TotalCount
We will apply Skip and Take to pData.Skip will skip no. of records of previous pages and Take will get no. of records you want to display in current page.
Using Skip and Take we will get only required No. of records for page.
After using this approach from API side, we will not require lazy loading from UI side because api will send data of single page for Grid.
It will also send TotalCount as total no. of records that helps you to manage pages on UI.We can use Math.ceil(TotalCount / PageSize), where it gets nearest large integer to get total pages.